Ethereum's layer-2 scaling solution, Polygon, is set to undergo a hard fork on January 17th, in order to tackle the issues of gas spikes and chain reorganization that have impacted the user experience on the Polygon proof-of-stake (POS) chain. The confirmation of the hard fork event was announced in a blog post on January 12th by Polygon, following weeks of discussions on the Polygon Improvement Proposal (PIP) forum page in December.
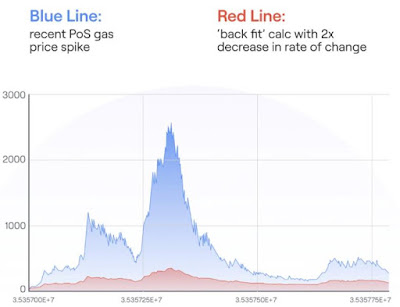
The Polygon Governance Team has voted in favor of implementing changes to reduce gas fee spikes and fix chain reorganization issues. 87% of the 15 voters approved increasing the BaseFeeChangeDenominator function from 8 to 16 and decreasing the SprintLength function from 64 blocks to 16. The Polygon Team explains that increasing the denominator from 8 to 16 will help "flatten the growth curve" and "smooth severe fluctuations" in gas prices which are often caused by rapid increases in on-chain activity.
The Polygon team has also addressed the issue of chain reorganization, by decreasing the sprint length. This will improve transaction finality, allowing a single block producer to add blocks at a faster frequency of 32 seconds, as opposed to the current 128 seconds. The team also emphasized that this change will not affect the total time or number of blocks a validator produces and there will be no change in rewards overall. However, chain reorganization increases the risk of a 51% attack, thus it must be done as efficiently as possible.
MATIC token holders and delegators will not be required to take any action during the hard fork and applications will not be affected. The price of Polygon's token, MATIC, is currently $0.977 and has seen a 13.6% increase since the announcement was made on January 12th.



.jpg)







0 Comments